Imagine a world where you can find out exactly what lies under your feet, get advanced warning of volcanic eruptions, look around corners or into rooms, and detect initial signs of multiple sclerosis.
Welcome to quantum detecting, an innovation that could change our reality.
At their heart, these sensors depend on the frequently confusing conduct of subatomic particles, where the established presumptions of Newtonian material science stop to exist.
"Quantum material science is said to be 'creepy', with particles being in two places without a moment's delay, yet it may be less creepy on the off chance that you consider them waves - and waves can be in a few places immediately," says Prof Kai Bongs of Birmingham University.
Prof Bongs' Birmingham group is a piece of a consortium of scholastics and organizations creating quantum gravity sensors or gravimeters that will be twice as delicate and multiple times as quick as present hardware.
This venture, marked Gravity Pioneer, could significantly improve how designers and surveyors plan and execute real development ventures.
Right now, the best way to discover what is underneath the ground is regularly to complete exploratory burrowing, which is both tedious and costly.
"Some have said that what lies underneath one meter under the avenues of London is less outstanding than Antarctica," says Prof Bongs.
This is a noteworthy cerebral pain for development organizations who need to complete reviews that can take days.
"There are a large number of mine poles in the UK, regularly two meters or less over, and if the highest point of the pole is five meters or more subterranean then they can't right now be identified," clarifies George Tuckwell of building administrations firm RSK, which is driving the Gravity Pioneer venture.
"Be that as it may, the new sensor will probably observe a large portion of them."
It utilizes rubidium molecules cooled by lasers to simply above total zero (- 273C) that are impelled upward in a vacuum and afterward estimated as they fall back under gravity.
It is so touchy it can distinguish the little variances in gravity that outcome from such moderately little underground structures.
This should help accelerate review times, says building firm Teledyne e2V, which is transforming Birmingham's model into a business show.
Cheaper sensors
Quantum detecting will likewise help in observing volcanoes.
Glasgow University specialists are working with Italian volcanologists to put a system of 40 minor gravimeters on Sicily's Mount Etna, a standout amongst the most dynamic volcanoes on the planet. As magma loads top off subterranean their gravity readings will change, in this way giving timely guidance of volcanic action.

Image Copyright: Getty Image
Italy's Mount Etna is one of the world's most active volcanoes
Researchers as of now utilize a variety of instruments -, for example, seismometers, ground mishappening recorders, gas screens, infrared cameras, and satellite imagers - to screen volcanoes.
Be that as it may, a system of shoddy and perpetual gravimeters is a potential distinct advantage, giving undeniably increasingly precise readings of magma developments.
"Basically, we will out of the blue have the capacity to give gravity imaging to long timespans," says Prof Giles Hammond at Glasgow's Institute of Gravitational Research.
Utilizing the present age of cumbersome non-quantum gravimeters implies researchers need to go on to the mountain and move them around - which has chanced on a functioning spring of gushing lava-like Etna.
The group is utilizing smaller scale and nano-creation procedures to make modest quantum gravimeters on silicon wafers that are multiple times less expensive than ordinary models.
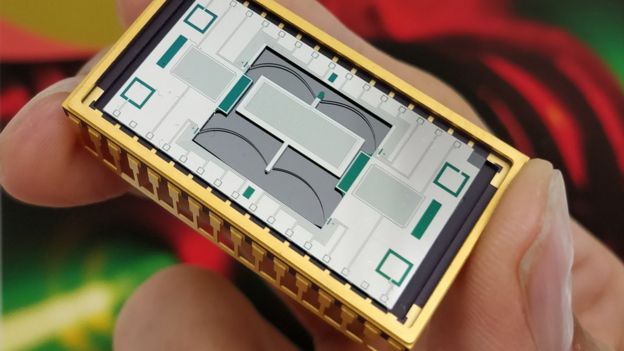
Picture copyright: GLASGOW UNIVERSITY
Glasgow's new gravimeter is little - and much less expensive than current models
"Our sensor is a mass on a delicate spring, and where that spring sits with a given mass is reliant on gravity. As gravity changes, where that spring sits additionally changes," clarifies Prof Hammond.
The college is likewise chipping away at an exceptional 3D sort of lidar that will empower you to look round corners, or "see" into a room.
Customary lidar estimates the separation to an article by enlightening it with beat laser light and after that estimating the reflected heartbeats. In any case, quantum innovation empowers researchers to quantify the entry time of single photons with exceptionally high precision, in trillionths of a second.
"In a gully, you'll hear your voice reverberation back," says Prof Daniele Faccio, head of Glasgow University's Extreme Light gathering.
"You can do likewise with light or a laser shaft. The light will bob off dividers - inasmuch as you have the geometry right. At that point, you can manufacture a 3D picture utilizing this information."
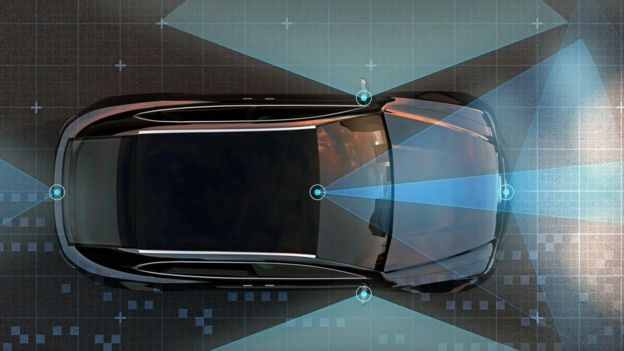
Picture copyright: Getty Images
Quantum sensors in vehicles will empower autos to see around corners
The point is to create cutting edge lidar for self-driving vehicles to give them improved mindfulness - through the haze, smoke and over longer separations.
Glasgow's model sensor would already be able to recognize moving individuals 100m away, notwithstanding when they're a couple of meters cycle a corner.
Health benefits
Our detection of degenerative diseases is also set to change thanks to quantum sensing.
While innovation like MRI [magnetic reverberation imaging] is as of now being used, quantum sensors are less difficult, less expensive and have better goals, says Sussex University's Prof Peter Kruger.
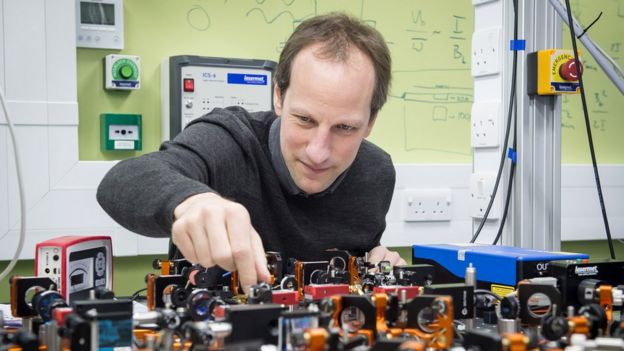
Picture copyright: SUSSEX UNIVERSITY
"Quantum tech is much more straightforward and less expensive and has better goals," says Peter Kruger
"In ailments like various sclerosis, the handling rate of the spinal rope to the mind changes. Be that as it may, existing instruments can't lift this up," he says.
"New quantum sensors would almost certainly recognize these adjustments in the manner in which that MRI sensor can't."
Stealthy Detection
As anyone might expect, militaries over the world are additionally backing examination into quantum detecting.
Gravimeters specifically offer the potential for recognizing your adversary's submarines, for example. Gravity might be a powerless power, yet you can't shield against it.
So while stealth innovation may shroud your radar signature, it won't conceal you from a quantum gravity sensor.
Last October, researchers at the US Army's RDECOM Research Laboratory in Maryland stepped forward in quantum detecting.
They utilized lasers to support Rydberg molecules (which are a lot bigger than ordinary particles) to uncommonly high vitality levels.
"This enormously builds the particle's affectability to electric fields. We've made a monster compass needle that is considerably more touchy than traditional ones," says Dr. Paul Kunz, some portion of the exploration group.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Paste Your Website and Article Link To Create Do-Follow Backlink