For a few years now it's been clear that Android dominates the mobile OS. This Java-based technology has sparked a new gold rush, with programmers competing to make money from their Android apps. Android jobs are also abundant, as shown by a quick job search using Indeed.com.
To be successful, Android developers need a good grasp of the Java language, Android APIs, and Android app architecture. It's also essential to use an appropriate and effective development environment. For many years, Eclipse IDE with the ADT plugin was the preferred platform for Android development. Today it's Android Studio.
If you're new to Android Studio, this tutorial series will get you started. I'll briefly introduce the Android development platform, then show you how to download, install, and run the software.
In this tutorial, we'll start up our first Android project and get to know the Android Studio project workspace. Next Tutorial we'll code the app, learn how to use Android Studio resources into the project to enter source code. At last, in Third Tutorial we'll build and run the app using an emulated hardware device.
Get started with Android Studio
he most recent stable version, 3.2.1, includes the following features:
- A unified environment where you can develop for all Android devices.
- Support for building Android TV apps and Android Wear apps.
- Template-based wizards to create common Android designs and components.
- A rich layout editor that lets users drag-and-drop user interface components and that offers an option to preview layouts on multiple screen configurations.
- Android-specific refactoring and quick fixes.
- Gradle-based build support.
- Lint tools to catch the performance, usability, version compatibility, and other problems.
- ProGuard integration and app-signing capabilities.
- A fast and feature-rich emulator.
- Instant Run to push changes to your running app without building a new APK (Application PacKage Zip file).
- Built-in support for Google Cloud Platform, enabling integration with Google Cloud Messaging and App Engine.
- C++ and NDK support.
- Plugin architecture for extending Android Studio via plugins.
Download Android Studio
Google provides Android Studio for the Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux platforms. You can download this software from the Android Studio homepage. Before downloading Android Studio, make sure your platform meets one of the following requirements:
Windows OS
- Microsoft Windows 7/8/10 (32-bit or 64-bit)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 8 GB RAM recommended
- 2 GB of available disk space minimum, 4 GB Recommended (500 MB for IDE + 1.5 GB for Android SDK and emulator system image)
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- JDK 8
- For accelerated emulator: 64-bit operating system and Intel processor with support for Intel VT-x, Intel EM64T (Intel 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality
Mac OS
- Mac OS X 10.8.5 or higher, up to 10.11.4 (El Capitan)
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 8 GB RAM recommended
- 2 GB of available disk space minimum, 4 GB Recommended (500 MB for IDE + 1.5 GB for Android SDK and emulator system image)
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- JDK 6
Linux OS
- GNOME or KDE desktop: Tested on Ubuntu 12.04, Precise Pangolin (64-bit distribution capable of running 32-bit applications)
- 64-bit distribution capable of running 32-bit applications
- GNU C Library (glibc) 2.11 or later
- 2 GB RAM minimum, 8 GB RAM recommended
- 2 GB of available disk space minimum, 4 GB Recommended (500 MB for IDE + 1.5 GB for Android SDK and emulator system image)
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
- JDK 8
- For accelerated emulator: Intel processor with support for Intel VT-x, Intel EM64T (Intel 64), and Execute Disable (XD) Bit functionality, or AMD processor with support for AMD Virtualization (AMD-V)
Once you've ensured your operating system is compatible with Android Studio 2.1.1, download the appropriate Android Studio distribution file. The Android Studio download page auto-detected that I'm running 64-bit Windows 8.1 and selected
android-studio-bundle-143.2821654-windows to download.Installing Android Studio on 64-bit Windows 8.1
I have launched to start the installation process of
android-studio-bundle-143.2821654-windows. The installer responded by presenting the Android Studio Setup dialog box shown in Figure 1.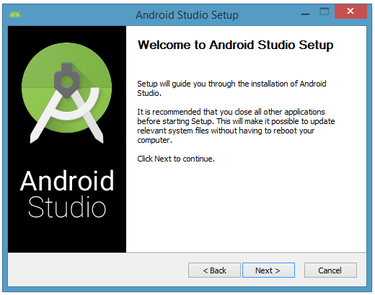
Clicking Next took me to the following dialog box, which gives you the option to decline to install the Android SDK (included with the installer) and an Android Virtual Device (AVD).
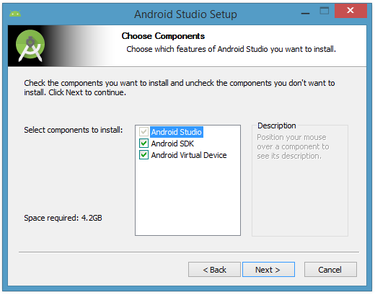
I chose to keep the default settings. After clicking Next, you'll be taken to the license agreement dialog box. Accept the license to continue the installation.
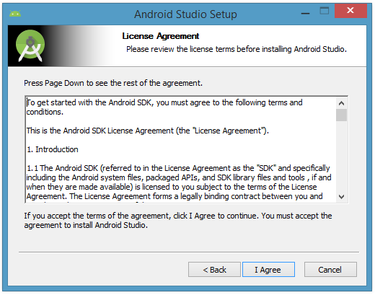
The next dialog box invites you to change the installation locations for Android Studio and the Android SDK
Change the location or accept the default locations and click Next.
The installer defaults to creating a shortcut for launching this program, or you can choose to decline. I recommend that you create the shortcut, then click the Install button to begin the installation.
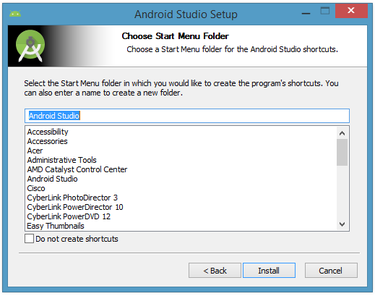
The resulting dialog box shows the progress of installing Android Studio and the Android SDK. Clicking the Show Details button will let you view detailed information about the installation progress.
The dialog box will inform you when the installation has finished. When you click Next, you should see the following:
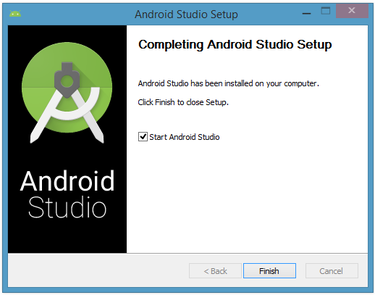
To complete your installation, leave the Start Android Studio box checked and click Finish.
Running Android Studio
Android Studio presents a splash screen when it starts running:

On your first run, you'll be asked to respond to several configuration-oriented dialog boxes. The first dialog box focuses on importing settings from any previously installed version of Android Studio.
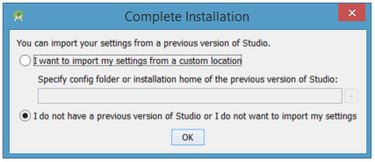
If you're like me and don't have a previously installed version, you can just keep the default setting and click OK. Android Studio will respond with a slightly enhanced version of the splash screen, followed by the Android Studio Setup Wizard dialog box:
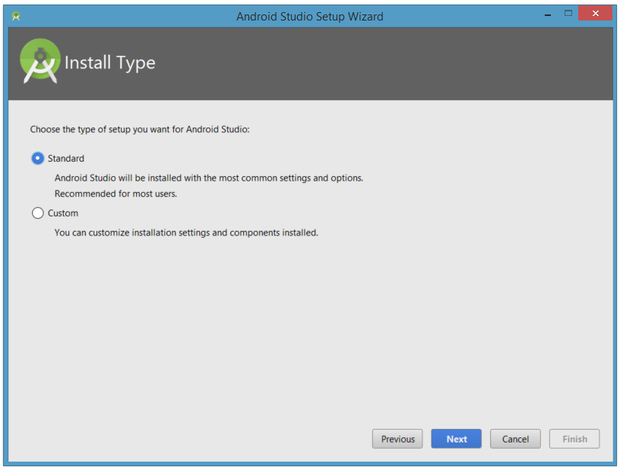
When you click Next, the setup wizard invites you to select an installation type for your SDK components. For now, I recommend you keep the default standard setting.
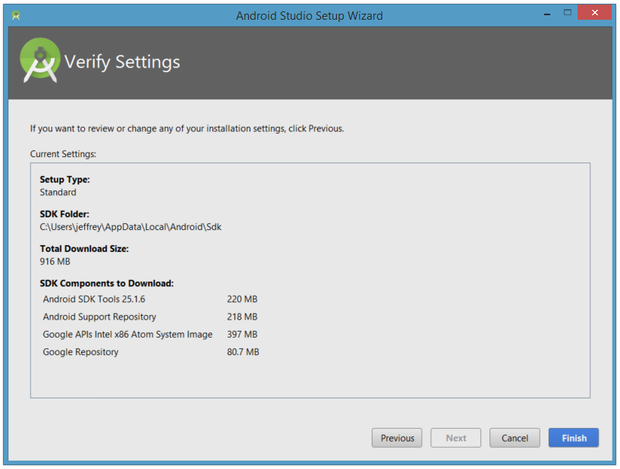
Click Next and verify your settings, then click Finish to continue.
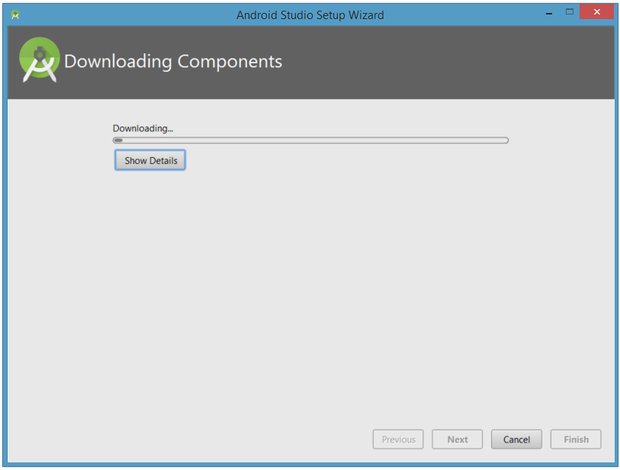
The wizard will download and unzip various components. Click Show Details if you want to see more information about the archives being downloaded and their contents.
If your computer isn't Intel-based, you might get an unpleasant surprise after the components have completely downloaded and unzipped:
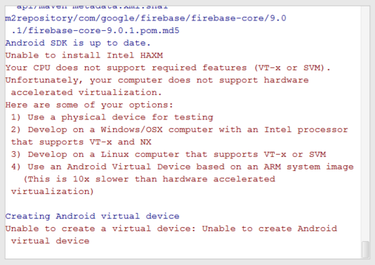
Your options are to either put up with the slow emulator or use an Android device to speed up development. I'll discuss the latter option later in the tutorial.
Finally, click Finish to complete the wizard. You should see the Welcome to Android Studio dialog box:

You'll use this dialog to start up a new Android Studio project, work with an existing project, and more. You can access it anytime by double-clicking the Android Studio shortcut on your desktop.
Your first Android Studio mobile app
The quickest way to get to know Android Studio is to use it to develop an app. We'll start with a variation on the "Hello, World" application: a little mobile app that displays a "Welcome to Android" message.
In the steps that follow, you'll start a new Android Studio project and get to know the project workspace, including the project editor that you'll use to code the app in Next Tutorial
Starting a new project
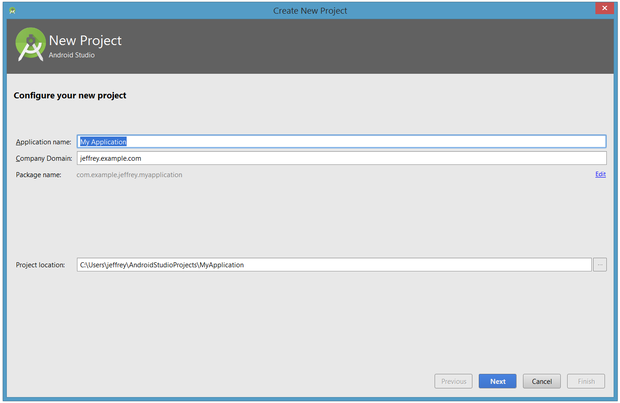
From our setup so far, you should still have Android Studio running with the Welcome to Android Studio dialog box. From here, click Start a new Android Studio project. Android Studio will respond with the Create New Project dialog box shown in Figure 15.
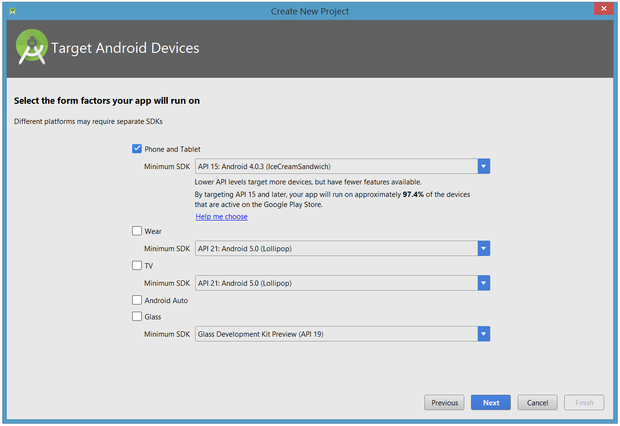
Enter the application name and the company domain name. Click Next to select your target devices.
Android Studio lets you select form factors, or categories of target devices, for every app you create. I would have preferred to keep the default API 15: Android 4.0.3 (IceCreamSandwich) minimum SDK setting. You can set up as your choice.
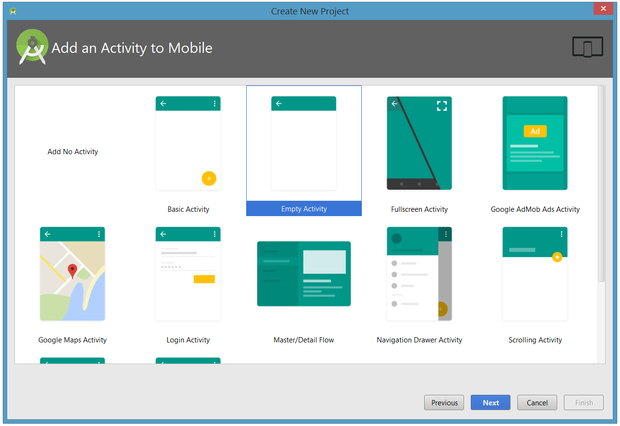
Click Next, and you will be given the opportunity to choose a template for your app's main activity. For now, we'll stick with Empty Activity. Select this template and click Next.
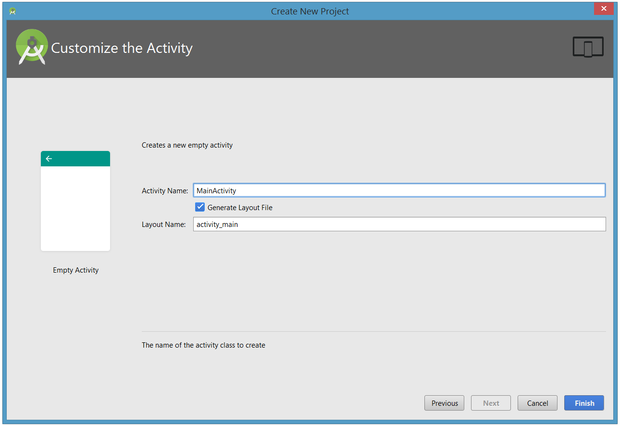
Next, you'll customize the activity:
Enter Application Name as the activity name and main as the layout name, and click Finish to complete this step. Android Studio will respond that it is creating the project, then take you to the project workspace.
The project workspace is organized around a menu bar, a toolbar, a work area, additional components that lead to more windows (such as a Gradle Console window), and a status bar. Also note the Tip of the Day dialog box, which you can disable if you like.
The project and editor windows
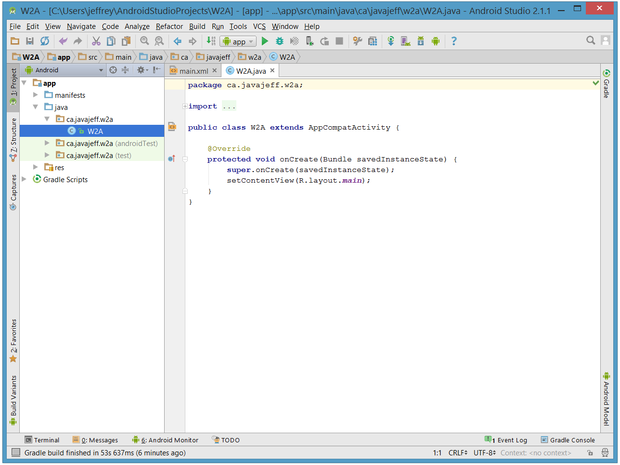
When you enter the project workspace, W2A is identified as the current project, but you won't immediately see the project details. After a few moments, these details will appear in two new windows.
The project window is organized into a tree whose main branches are App and Gradle Scripts. The App branch is further organized into manifests, java, and res subbranches:
- manifests stores,
AndroidManifest.xmlwhich is an XML file that describes the structure of an Android app. This file also records permission settings (where applicable) and other details about the app. - java stores an app's Java source files according to a package hierarchy, which is
ca.javajeff.w2aasin this example. - res stores an app's resource files, which are organized into drawable, layout, mipmap, and values subbranches:
- drawable: an initially empty location in which to store an app's artwork
- layout: a location containing an app's layout files; initially,
main.xml(the main activity's layout file) is stored here - mipmap: a location containing various
ic_launcher.pngfiles that store launcher screen icons of different resolutions - values: a location containing,
colors.xmldimens.xml,strings.xmlandstyles.xml
The Gradle Scripts branch identifies various
.gradle (such as build.gradle) and .properties (such as local.properties) files that are used by the Gradle-based build system.Conclusion:
You've installed and configured Android Studio and created a project for your first Android Studio mobile app. Now, you're ready to build your Android application. Click Here when you're ready to get started with your first Android animated mobile app.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Paste Your Website and Article Link To Create Do-Follow Backlink